GnRH Antagonists: Suppress the production of hormones, often used for fertility treatments.
Brief information about it:
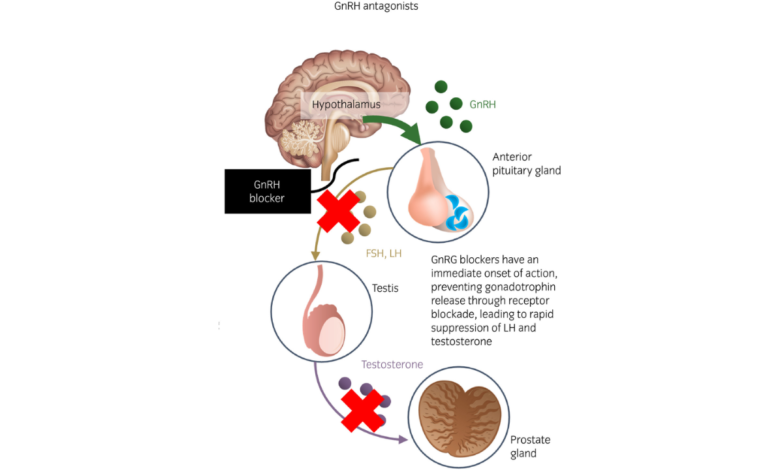
GnRH antagonists are medications that suppress the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a hormone that stimulates the production of other hormones involved in reproduction. They are often used in fertility treatments, particularly in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Uses:
· Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): GnRH antagonists are used to suppress the production of natural hormones, allowing for controlled stimulation of the ovaries with other medications. This is often done to prepare women for egg retrieval in IVF.
· Endometriosis: GnRH antagonists can be used to treat endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus.
· Precocious puberty: They can be used to delay puberty in children who experience it too early.
Mechanism of action:
GnRH antagonists bind to GnRH receptors in the pituitary gland, blocking the release of GnRH. This prevents the pituitary gland from stimulating the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone.
Elimination half life:
The elimination half-life of GnRH antagonists can vary depending on the specific medication. It is generally excreted from the body within 24-48 hours.
Route of Administration:
GnRH antagonists are typically administered as injections, either subcutaneously (under the skin) or intramuscularly (into the muscle).
Side effects:
· Hot flashes: Hot flashes are a common side effect of GnRH antagonists.
· Vaginal dryness: Vaginal dryness can occur due to the suppression of estrogen production.
· Headaches: Headaches may occur in some individuals.
· Mood changes: Mood swings or depression can be experienced by some.
· Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS): In rare cases, GnRH antagonists can contribute to OHSS, a condition where the ovaries become overstimulated.
Dose:
The dosage of GnRH antagonists varies depending on the specific medication, the reason for use, and individual factors. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage for you.
Precautions:
· Consult a doctor: Before using GnRH antagonists, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe for you and to discuss potential risks and benefits.
· Pregnancy: GnRH antagonists should not be used during pregnancy.
· Breastfeeding: If you are breastfeeding, consult with your doctor before using GnRH antagonists.
· Allergic reactions: Inform your doctor if you have any allergies to medications or other substances.





