Blog
PCOS Treatment: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches
PCOS Treatment: Managing Symptoms and Improving Health
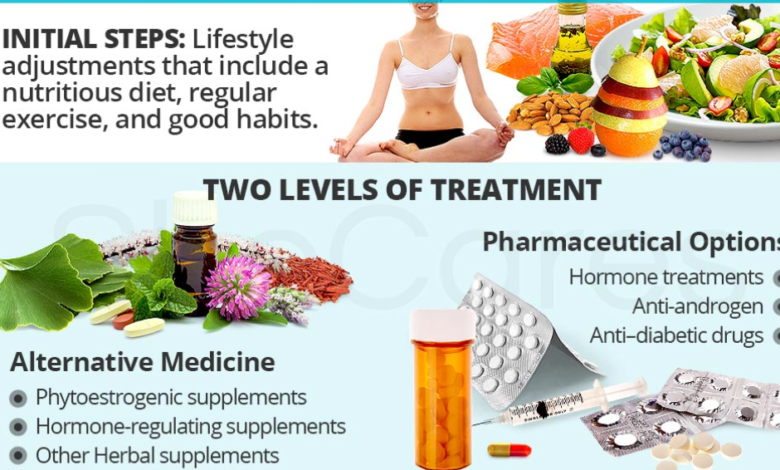
Managing PCOS often involves a combination of medical and lifestyle approaches tailored to address individual symptoms and health goals.
Medical Treatments
- Hormonal birth control: Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve acne and hirsutism.
- Metformin: This medication, typically used for type 2 diabetes, can improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and aid in weight management.
- Anti-androgen medications: These medications can block the effects of androgens, helping to reduce hirsutism, acne, and hair loss.
- Ovulation induction medications: Medications like clomiphene citrate or letrozole can stimulate ovulation for women trying to conceive.
- Fertility treatments: If medication is not successful, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be an option.
Lifestyle Changes
- Weight management: Even modest weight loss (5-10%) can significantly improve insulin sensitivity, regulate periods, and improve fertility.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in whole foods, complex carbohydrates, lean protein, healthy fats, and fiber can help manage insulin resistance, promote weight loss, and reduce inflammation.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and can improve mood and reduce stress.
- Stress management: Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and adequate sleep can help manage stress, which can worsen PCOS symptoms.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The most appropriate treatment plan for PCOS depends on individual symptoms, health goals, and preferences. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan.
Important Considerations:
- No one-size-fits-all approach: Treatment plans should be tailored to each individual.
- Long-term management: PCOS is a chronic condition that often requires long-term management.
- Regular follow-up: Regular check-ups with your doctor are important to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Causes of PCOS
- Insulin resistance.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Low-grade inflammation.
- Genetics.
PCOS Symptoms
Physical Symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Hirsutism.
- Acne.
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Hair loss.
- Skin problems.
- Polycystic ovaries.
- Infertility.
Emotional Symptoms:
- Mood swings.
- Anxiety.
- Depression.
- Body image issues.
The Role of Diet in PCOS
- Focus on whole foods.
- Prioritize complex carbohydrates.
- Include lean protein.
- Choose healthy fats.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
- Consider a low glycemic index (GI) diet.
- Increase fiber intake.
- Consume anti-inflammatory foods.





